For a Better Tomorrow!
Seoul Ahnkang Hospital is Here with You.

Rehabilitation Assessment
Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography is a test that analyzes electrical signals generated from nerves and muscles using a machine to check for abnormalities in peripheral nerves, neuromuscular junction, and muscles.

Electromyography has a nerve conduction test to check for peripheral nerve damage by applying electrical stimulation to the skin along the pathways of motor and sensory nerves and a test to check for muscle damage using needles.
Recently, evoked potential testing, which tests the peripheral nerves to the central nerves through somatosensory, motor, hearing, and vision, is performed to determine whether there is damage to the peripheral and central nervous systems.
[ Inspections for EMG ]
- -
Coldness, numbness, dullness in hands and feet
- -
Tremors or twitching of hands and feet
- -
Posterior neck and back pain
- -
Muscle weakness or paralysis
- -
Diseases of the peripheral and central nervous system
- -
Muscle diseases

[ EMG Preparation & Precautions ]
- ·
Prepare so the skin temperature in the test area is not too cold.
- ·
If you have foreign substances such as lotion or cream on your skin, the test will take longer, so it is best to come without them.
- ·
If you are taking medications that may cause bleeding, such as thrombolytics (drugs that dissolve blood clots), or if you have hemophilia, which tends to bleed, you must inform us before the test.
- ·
Even if you have a cardiac pacemaker sensitive to electrical stimulation, you must inform the patient before the test.
Pregnant women in the early stages must also inform the patient before the test. - ·
During needle electromyography, a needle is inserted into the muscle, so temporary pain, swelling, or bleeding may occur at the insertion site.
Musculoskeletal Ultrasonogram
Musculoskeletal ultrasound examination allows for a detailed assessment of the pathological conditions of the
joints and surrounding ligaments in the upper and lower
extremities, including the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, hip joint, knee, ankle, and foot.
It is also a useful test for diagnosing masses in body parts or muscle tears.

Inflammation of the joints, damage to the surrounding ligaments, and inflammation or degenerative changes of tendons can be accurately diagnosed through a musculoskeletal ultrasound examination.
This examination is particularly useful as it allows for joint movement during the assessment, enabling the diagnosis of abnormalities that are only visible in specific positions.
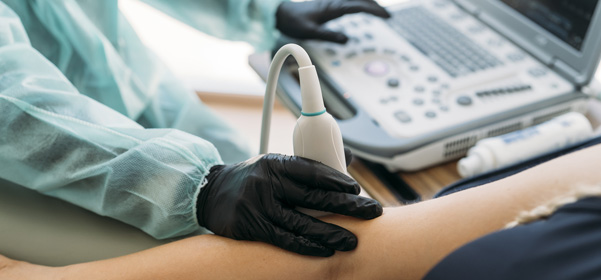
In addition, a musculoskeletal ultrasonogram can be performed in real-time during injection treatment, making it an effective technique for accurately observing and treating damaged or inflamed areas.
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study
(VFSS)
It is a test performed by chewing or swallowing food of various properties
with different viscosity mixed with contrast agents or water mixed with contrast agents under
fluoroscopy.
It is a tool for accurately observing the process of food going down
to the oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus to determine whether there is a swallowing disorder.

This test evaluates the degree of dysphagia. It is an effective tool for determining the most appropriate swallowing method, posture, and diet for patients with dysphagia by simultaneously examining several postures and compensatory methods.